Huntington vs Parkinson
2/21/24, 10 mins reading
As another basal ganglia disorder, Huntington’s disease shares a lot with Parkinson’s disease in terms of causes, symptoms, treatments, etc. For instance, both are neurodegenerative disorders in which neurons get damaged and die over time, and the condition will get worse and worse as the condition progresses. Both disorders could occur in young people. Both present motor symptoms and non-motor symptoms. Both disorders are treatable, but not curable. However, there are a slew of differences between these two disorders.
Prevalence. With 0.3% prevalence in industrialized countries, Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease behind Alzheimer’s disease. While Huntington’s disease is much less common with only a prevalence of 0.01%.
Cause. There are still no known causes for Parkinson’s disease, it is believed that both genetic and environmental elements contribute to it. The majority of cases of Parkinson’s disease are idiopathic and sporadic although Gene mutations such as LRRK2 have been found in families. Nonetheless, Gene HTT has been identified and confirmed to be the cause of Huntington’s disease.
Gender. In Parkinson’s disease, Men are two times more likely than women to develop. It is unknown why there is a gender difference in terms of incidence. In Huntington’s disease, both men and women have an equal incidence of developing Huntington’s disease.
Onset age. A large number of Parkinson’s disease patients are diagnosed at the age of 50 or older with an average age of 60. However, Huntington’s disease patients are diagnosed at a younger age with the majority of 30-55.
Brain region. The signature area involved in Parkinson’s disease is the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc)in the midbrain. The death of dopamine-produced neurons from SNpc is the major pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. On the other hand, the brain region involved in Huntington’s disease is the striatum, which accepts projections from neurons in SNpc and forms the nigrostriatal pathway. Both SNpc and striatum are parts of the basal ganglia.
Symptoms. Generally speaking, Both Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease present motor and no motor symptoms. Nonetheless, hand shaking in Parkinson’s disease is rhythmic and constant, it occurs in fingers or hands. On the other hand, handshaking in Huntington’s disease is jerking, and dancelike, and it occurs in hands, and fingers first, and more likely extends to the whole body.
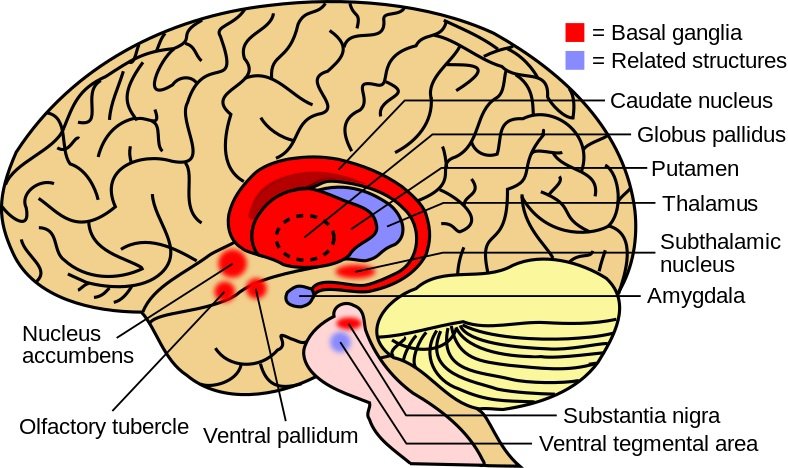
Keyword: basal gangliaThe Basal ganglia is a cluster of cells located deep in the brain. It has been associated with a multitude of functions including motor, cognition, and reward. Structurely speaking, it includes the striatum(dorsal striatum: caudate nucleus and putamen, and the ventral striatum: nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum, the substantia nigra, and the subthalamic nucleus. The dysfunctions in basal ganglia could lead to Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease.
Basal ganglia structure in the human brain.